Content

Current liabilities include all liabilities that are expected to be paid within one year. Any liabilities with a payment period of over a year are considered long-term. Generally speaking, the lower the debt ratio for your business, the less leveraged it is and the more capable it is of paying off its debts.
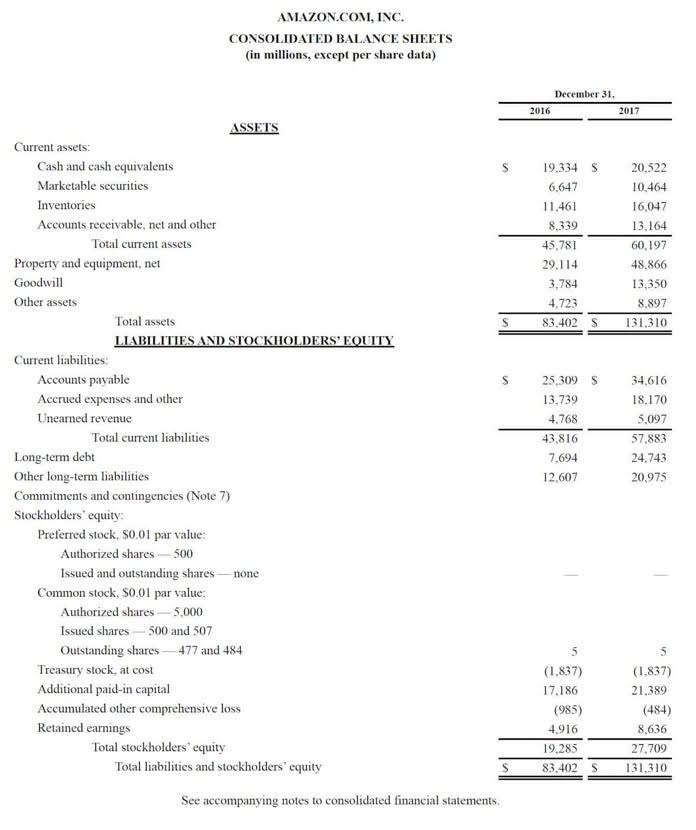
Assets are classified in terms of convertibility, usage, and physical existence. Assets can be either current or non-current (convertibility), operating or non-operating (usage), and tangible or intangible (physical existence). Harold Averkamp https://accounting-services.net/quicken-estate-and-trust-fiduciary-accounting/ (CPA, MBA) has worked as a university accounting instructor, accountant, and consultant for more than 25 years. He is the sole author of all the materials on AccountingCoach.com. Check out Forage’s free finance virtual experience programs.
Liabilities vs. Expenses
More detailed definitions can be found in accounting textbooks or from an accounting professional. Xero does not provide accounting, tax, business or legal advice. Liabilities are any debts your company has, whether it’s bank loans, mortgages, unpaid bills, IOUs, or any other sum of money that you owe someone else. When a company deposits cash with a bank, the bank records a liability on its balance sheet, representing the obligation to repay the depositor, usually on demand. Simultaneously, in accordance with the double-entry principle, the bank records the cash, itself, as an asset. The company, on the other hand, upon depositing the cash with the bank, records a decrease in its cash and a corresponding increase in its bank deposits (an asset).
Long-term liabilities refer to all liabilities that aren’t due in full within the year. This group can include loans, deferred tax obligations and any pension payments. Also sometimes called “non-current liabilities,” these are any obligations, payables, loans and any other liabilities that are due more than 12 months from now.
What Is a Contingent Liability?
When the supplier delivers the inventory, the company usually has 30 days to pay for it. This obligation to pay is referred to as payments on account or accounts payable. The liabilities component of the balance sheet helps businesses increase their value creation and organize business operations processes.
- Each person should consult his or her own attorney, business advisor, or tax advisor with respect to matters referenced in this post.
- Liabilities are incurred in order to fund the ongoing activities of a business.
- These are liabilities that are event dependent and are not always sure to occur.
- Dive in for free with a 10-day trial of the O’Reilly learning platform—then explore all the other resources our members count on to build skills and solve problems every day.
- They reflect amounts owed to various parties, and serve as an offset to held assets in determining the net worth of a person or entity.
You might take out a small business loan (a liability) to purchase the software (an asset). Liabilities are the debts you owe to other parties, including other businesses or the government. While liabilities Similarities & Differences Between Accounting & Bookkeeping seem negative at first, they can be very important for growth. For example, a Small Business Association (SBA) loan is a liability, but can provide much-needed funds for a budding small business owner.
Noncurrent liabilities
Liabilities are reported on a company’s balance sheet along with its assets and owners’ equity. Liabilities in accounting are categorized depending on when they are due or must be paid. The two main types of liabilities are short-term liabilities and long-term liabilities. Short-term liabilities are the debts or obligations due within the current period, which is usually one year. This means the bills and other debts owed must be paid within this period. This includes any obligations owed to other businesses, lenders, or customers.
The current month’s utility bill is usually due the following month. Once the utilities are used, the company owes the utility company. These utility expenses are accrued and paid in the next period. Accounts Payable – Many companies purchase inventory on credit from vendors or supplies.
Build your dream business for $1/month
Your business has unearned revenue when a customer pays for goods or services in advance. Then, the transaction is complete once you deliver the products or services to the customer. Paying off your debts helps lower your business’s liabilities.

Liabilities are settled over time through the transfer of economic benefits including money, goods, or services. Bonds Payable – Many companies choose to issue bonds to the public in order to finance future growth. Bonds are essentially contracts to pay the bondholders the face amount plus interest on the maturity date.